
- While it plays a vital role in healing, chronic inflammation can contribute to serious health issues.
- Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods like mackerel, olive oil, dark chocolate and avocados can help combat inflammation and promote overall health.
- Simple adjustments to your daily habits and meals can make a meaningful difference in reducing inflammation and supporting long-term well-being.
Inflammation is an inevitable part of life. It is your body’s natural response to trauma, infections, injuries and toxins, acting as a defense mechanism to protect your health. While it may sound unpleasant, acute inflammation plays a critical role in healing by targeting foreign invaders and helping your body recover. However, when inflammation lingers and becomes chronic, it can lead to serious health issues such as cancer, diabetes, and Alzheimer’s. Factors like excessive alcohol consumption and diets high in saturated fats can exacerbate inflammation.
The good news is that you can take steps to combat inflammation and reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases. While there’s no single food that can work as a cure-all, adopting a diet inspired by the Mediterranean diet is a highly effective approach. This eating pattern prioritizes whole, nutrient-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, lean proteins and whole grains, while emphasizing healthy fats from sources such as nuts, olive oil and fish. By making these dietary changes, you can give your body the tools it needs to fight inflammation and support long-term health.
1. Mackerel
Mackerel is an oily fish that is a source of two omega-3 fatty acids: EPA and DHA. One study took a close look at the effects of diets rich in oily fish and their impact on inflammation in people at risk for cardiometabolic diseases like type 2 diabetes and heart disease, and results showed that diets rich in oily fish effectively lowered plasma C-reactive protein, a marker of inflammation that can serve as a commonly-used sign of future cardiovascular problems. Moist, flaky and slightly salty describe mackerel’s distinct flavor and texture. And just one 3-ounce piece delivers significant amounts of calcium, vitamin D, vitamin A and choline. Holy mackerel! There’s no shortage of nutrition with this fatty fish. You can top your lunch salad with flaked wild-caught mackerel from a can or grill some mackerel for dinner to keep your health at the forefront.
2. Olive Oil
Over the years, the good news of olive oil’s benefits and versatility has almost everyone drizzling it on anything from roasted root vegetables to freshly popped popcorn. As a cornerstone of the Mediterranean diet and a key player in its inflammatory benefits, olive oil has long been studied in heart-health research. Compared to other plant-based oils, olive oil is the richest in monounsaturated fats, which lower LDL (bad) cholesterol while raising HDL (good) cholesterol levels. Moreover, other data showed that dosing yourself with more than a half-tablespoon of olive oil daily could lessen the risk of heart disease. Olive oil contains a phenolic compound called oleocanthal, which targets inflammation and other diseases, giving us yet one more reason to love olive oil.
3. Dark Chocolate
While dark chocolate is known for its unique bitter flavor, what it lacks in sweetness, it makes up for in antioxidants. Antioxidants, like the flavonols in chocolate, are known inflammatory fighters. That said, dark chocolate is also a source of anti-inflammatory fats. Oleic acid, the fatty acid in olive oil, makes up 33% of dark chocolate. Oleic acid has improved inflammation in multiple body organs, including the eyes, skin, lungs, digestive tract and liver. It has also been shown to reduce pro-inflammatory markers and activate the immune system. If you need any further motivation to get your chocolate fix, we have you covered. Just make sure it’s at least 70% dark chocolate; the greater the percentage, the better the anti-inflammatory power. Also, keep in mind that dark chocolate may contain heavy metals, so make sure to choose the best options and moderate your consumption.
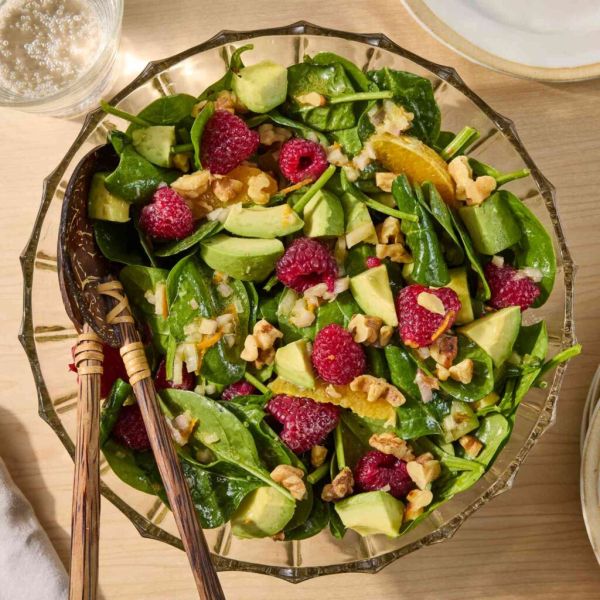
4. Avocados
What’s creamy, green on the inside and chock-full of nutrients like potassium and folate? Avocados! And they have gained massive popularity over the last decade (hello, avocado toast). Like olive oil, this superfood fruit is a source of monounsaturated fats (MUFAs), helping to keep the heart healthy. While eating high amounts of saturated fatty acids may make you prone to inflammation, monounsaturated fats show the opposite effect. Data shows that people who follow the Mediterranean diet, which is high in MUFAs, have lower levels of inflammation than those following a typical Western diet. Furthermore, avocados provide vitamin E, which functions as an antioxidant and can help reduce inflammation.
5. Flaxseed
Flaxseeds are small but mighty when it comes to nutrition! These tiny seeds pack a punch of plant-based omega-3 fats, making them a fantastic addition to your diet. Known for their rich fiber content and plant lignans, or natural compounds found in a variety of plants that function as antioxidants and phytoestrogens, flaxseeds are a health powerhouse. A 2020 review in Cytokine analyzed 40 studies with 2,520 participants and found that flaxseed supplementation improved inflammatory markers.
For the best results, go for ground flaxseeds so your body can fully absorb their benefits. Or try flaxseed oil when you are cooking to reap some of the benefits flaxseeds offer. Incorporating these nutrient-dense seeds into your routine is a simple and delicious way to enhance your immunity and fight inflammation.
6. Edamame
A staple food for many vegetarians and vegans, edamame are immature soybeans that make a tasty, filling snack with a pinch of salt. While edamame is often touted for its protein and fiber, the bright green legume also contains MUFAs, polyunsaturated fats and isoflavones—a perfect storm for warding off inflammation. One cup of edamame offers significant nutrients, including choline, folate, vitamin A, calcium, lutein and zeaxanthin, for healthy vision. Soy products, especially natural ones like soybeans or soy milk, could reduce CRP levels, a key sign of inflammation, by about 9%, according to results of a meta-analysis.
7. Walnuts
Health experts and researchers agree that eating tree nuts can help thwart inflammation and preserve cholesterol levels and heart health. As soon as you bite into a walnut, you’ll note its oily texture, which is thanks to its massive levels of good-for-you fats like omega-3s. Walnuts possess an impressive set of nutrients like alpha linolenic acid (ALA), a plant-based omega-3 fatty acid that has been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties. Fun fact: walnuts are the only tree nut that is considered an “excellent” source of ALA omega-3 fatty acids.
Anti-Inflammatory Recipes to Try
Our Expert Take
Inflammation is a natural and necessary part of your body’s defense mechanism, but chronic inflammation can have serious consequences for your health. The good news is that adopting a lifestyle and diet centered around anti-inflammatory foods and healthy habits can make a positive difference. By incorporating nutrient-rich options like mackerel, extra-virgin olive oil, dark chocolate, avocados, flaxseed, edamame and walnuts into your meals, you can take proactive steps to reduce inflammation and boost your overall well-being. Small, consistent changes in your diet and daily routine can empower your body to thrive and protect itself, one healthy choice at a time.
-
The #1 Snack to Buy at Costco for More Energy

-
Rakhi Sawant Backs Diljit Dosanjh Amid Sardaar Ji 3 Row, Cheers Hania Aamir’s Bollywood Debut

-
Deepshika Nagpal Says Shefali Jariwala and Parag Tyagi was madly in love

-
Varun Dhawan slams paps for insensitive coverage of Parag Tyagi crying holding wife Shefali Jariwala’s ashes

-
Sitare Zameen Par Collection Day 9: Aamir Khan’s 7th film was included in 100 crore club, know how much earned earnings …
