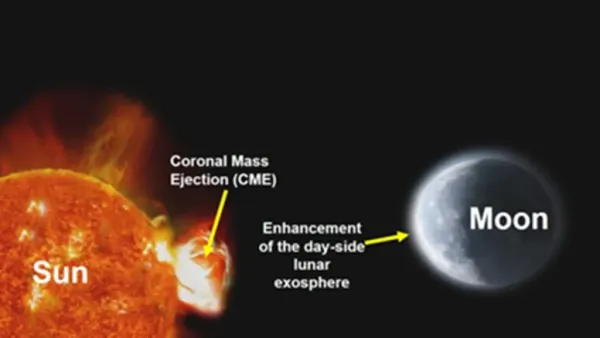
New Delhi. In a historic scientific breakthrough, the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) has announced that its Chandrayaan-2 has for the first time observed the effects of Coronal Mass Ejection (CME) from the Sun on the Moon using its scientific instrument. This is an unprecedented achievement that no other space agency in the world has ever achieved before.
Read:- US launched a major attack on China’s National Time Service Center, Dragon suffered huge damage
This observation will help in understanding the influence of space weather on the Moon’s exosphere and thin atmosphere and its surface. India’s Chandrayaan-2 orbiter has achieved a historic feat, detecting for the first time how a solar storm (Coronal Mass Ejection – CME) affects the Moon’s exosphere. The CHACE-2 (Chandra Atmospheric Composition Explorer-2) instrument mounted on Chandrayaan-2 made this historic discovery. During a rare solar event that occurred on May 10, 2024, a series of CMEs impacted the Moon.
This resulted in a dramatic increase in the total pressure of the outer atmosphere of the Moon’s day side. ISRO scientists reported that the number density of neutral atoms and molecules in the exosphere increased by more than a decade, which was earlier limited to only theoretical estimates. This discovery is not only a matter of pride for India’s space science, but it also provides important data for future moon missions and space weather research.
-
Australia foil RoKo show to etch seven-wicket win over India in 1st ODI

-
Food vendors wash food containers in basin; Indian Railways clarifies

-
Smriti Mandhana to marry Palash Muchhal, Bollywood composer

-
Delhi Police steps up security, traffic measures across markets, public places ahead of Diwali

-
Defence Tech Startup Tonbo Imaging's FY25 Profit Increases 6% To INR 73 Cr
